
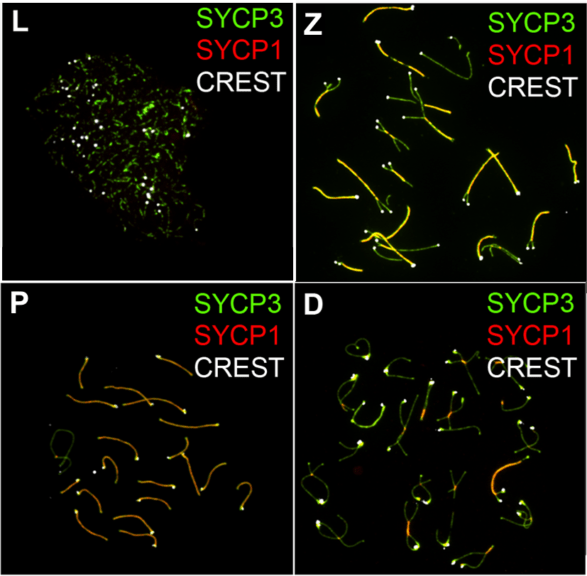
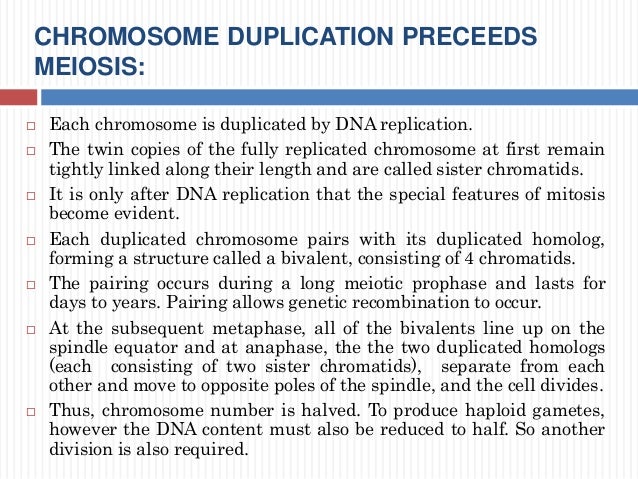
As the chromosomes condense they get shorter and thicker and can be seen through the microscope as individual structures (Fig. This change in chromosome structure makes them easier to move around the cell, an important structural change for what is about to happen. In prophase, the chromosomes in the nucleus change from being loosely dispersed to becoming more condensed. It is difficult to pick out an individual chromosome because they are each so spread out. Remember that chromosomes are replicated during the S phase of Interphase and replication of the chromosomes is possible because they are dispersed. During interphase, the chromosomes are loosely dispersed in the nucleus. Chromosomes become more coiled and can be viewed under a light microscope.Prophase is the beginning of mitosis. What events occur during prophase? Chromosomes become visible, the nucleolus disappears, the mitotic spindle forms, and the nuclear envelope disappears. Chromosomes become visible,or in other words they condense. Metaphase: Chromosomes move to the center of the cell and live up along the cell’s midline. Also, centrioles form and spindle fibers stretch across the cell. Prophase: The cell’s nuclear membrane disappears and the chromatin coils into tightly packed structures called chromosomes. Prophase I The first is the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes that can be seen through the microscope the second is the synapsis or physical contact between homologous chromosomes and the crossing over of genetic material between these synapsed chromosomes. What happens during telophase I? What happens in prophase 1 and 2 of meiosis? After cytokinesis, the two daughter cells would have genetically different chromosomes after meiosis I. This will then be followed by cytokinesis producing two daughter cells. Telophase I is that phase when the chromosomes have finished moving to opposite ends of the cell. The main events of prophase are: the condensation of chromosomes, the movement of the centrosomes, the formation of the mitotic spindle, and the beginning of nucleoli break down.

During prophase, the complex of DNA and proteins contained in the nucleus, known as chromatin, condenses. Prophase is the first phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. The main difference between prophase 1 and 2 is that genetic recombination occurs through crossing overs and the “Chiasmata” formation during prophase 1 whereas no genetic recombination is noticed at the prophase 2. What happens during prophase I of meiosis? Homologous chromosomes form and crossing over occurs between them. What happens during prophase 1 of meiosis quizlet? Thus, this stage is important to increase genetic variation. Prophase I highlights the exchange of DNA between homologous chromosomes via a process called homologous recombination and the crossover at chiasma(ta) between non-sister chromatids. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope (the membrane surrounding the nucleus) breaks down. The first and longest phase of mitosis is prophase.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
